Xenoestrogens & Hormone Disruptors: How to Identify, Avoid, and Detox
Hormones are your body’s chemical messengers, controlling everything from your mood and metabolism to growth and reproduction. But in today’s world, synthetic chemicals called xenoestrogens can disrupt these delicate systems. Found in everything from plastics to personal care products, xenoestrogens mimic natural estrogen, throwing your body’s hormonal balance off course.
If you’ve never heard of xenoestrogens before, this article will explain what they are, why they’re harmful, and, most importantly, how you can reduce your exposure. Whether you’re looking to improve your overall health or address specific hormone-related concerns, these tips and resources will help you make informed choices.
From a functional and environmental health perspective, reducing xenoestrogen exposure is one of the most impactful ways to support hormone balance, fertility, and long-term metabolic health.
What Are Xenoestrogens?
Xenoestrogens are synthetic chemicals that act like estrogen in the body. Unlike naturally occurring estrogens, xenoestrogens overstimulate or block hormone receptors, leading to hormonal imbalance. Over time, chronic exposure can contribute to health problems such as:
Hormonal Imbalances: Symptoms include mood swings, fatigue, acne, or weight gain.
Reproductive Issues: Irregular periods, infertility, or early onset puberty.
Increased Cancer Risk: Particularly estrogen-sensitive cancers like breast and ovarian cancer.
Metabolic Disruption: Difficulty losing weight or unexplained weight gain.
Xenoestrogens are not the sole cause of cancer, but they are a well-documented contributing factor to estrogen-driven disease processes.
Common Sources of Xenoestrogens
Xenoestrogens are hidden in many everyday products, often without clear labeling. Here’s where they’re commonly found:
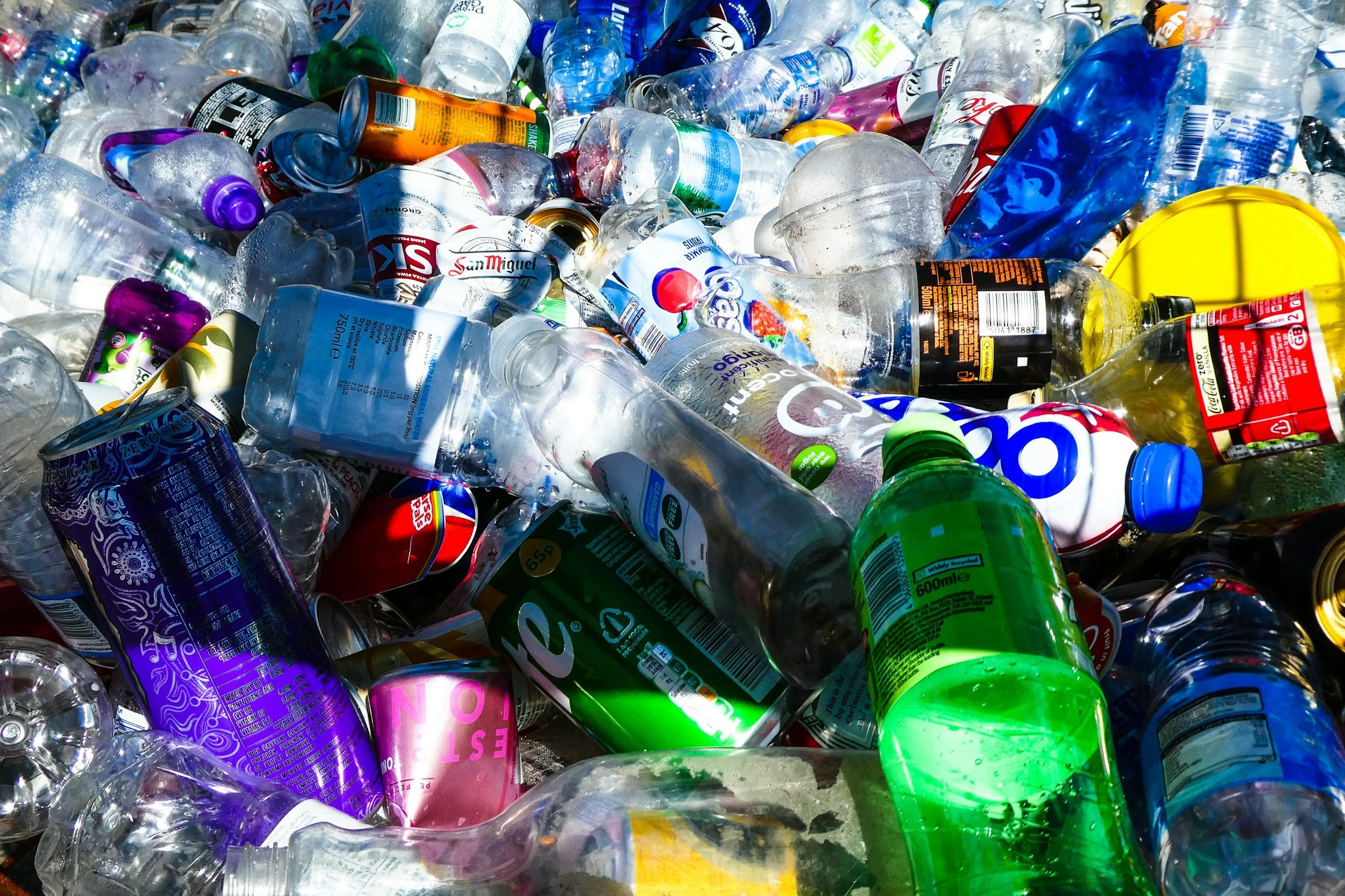
Plastics
Bisphenol A (BPA) and its alternatives (BPS, BPF): Found in water bottles, food containers, and plastic wraps.
Heat increases leaching, so microwaving or storing hot foods in plastic is especially problematic.
Personal Care Products
Parabens and Phthalates: Used as preservatives and fragrance carriers in shampoos, lotions, and makeup.
Household Items
Synthetic Fragrances: Found in air fresheners, laundry detergents, and fabric softeners.
Food and Water
Pesticides and Herbicides: Non-organic produce may be contaminated.
Hormones in Conventional Meat and Dairy: Factory-farmed animal products often contain added estrogen.
Tap Water: Can be contaminated with industrial pollutants and plastic-derived chemicals.
How Xenoestrogens Interact with Other Environmental Toxins
Xenoestrogens do not work alone—they interact with other environmental toxins to create a compounded endocrine-disrupting effect.
Heavy Metals (Mercury, Lead, Cadmium, Arsenic): These toxins impair the liver’s ability to detoxify xenoestrogens, leading to increased accumulation in the body.
PFAS (Forever Chemicals): Found in non-stick cookware, water-resistant fabrics, and fast-food packaging, PFAS are known endocrine disruptors that amplify the effects of xenoestrogens.
Airborne Pollutants: Industrial chemicals in air pollution have been found to alter estrogen metabolism, worsening the impact of xenoestrogens.
Because these toxins often work synergistically, reducing xenoestrogen exposure is only part of the solution—it’s equally important to detox from other harmful environmental chemicals.
Signs of Hormonal Imbalance from Xenoestrogens
If xenoestrogens are disrupting your hormones, you might experience one or more of the following symptoms:
For Women:
Irregular or heavy menstrual cycles
Breast tenderness or fibrocystic breasts
PMS symptoms, mood swings, or anxiety
Fertility issues or difficulty conceiving
Early onset of puberty
Increased fat storage around the thighs and hips
For Men:
Lower testosterone levels
Increased belly fat and difficulty building muscle
Gynecomastia (enlarged breast tissue)
Low libido and erectile dysfunction
Fatigue and brain fog
For Both Genders:
Unexplained weight gain
Persistent fatigue
Chronic headaches or migraines
Thyroid dysfunction (hypothyroidism or Hashimoto’s disease)
Sleep disturbances or night sweats
If you’re experiencing multiple symptoms, testing for hormone imbalance may help determine if xenoestrogens are playing a role.
Best Tests for Identifying Xenoestrogen Exposure
If you suspect xenoestrogen exposure is affecting your health, the following tests can help assess your hormone levels:
DUTCH Test (Dried Urine Test for Comprehensive Hormones)
Measures estrogen metabolites, which indicate whether xenoestrogens are overloading your system.
Also evaluates cortisol, melatonin, and progesterone levels.
Salivary Hormone Test
Measures bioavailable (active) levels of estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone.
Helps assess estrogen dominance.
Blood Serum Hormone Panel
Tests for total and free estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, and thyroid function.
Best for assessing baseline hormone levels.
Liver Function Test (ALT, AST, Bilirubin)
Since the liver is responsible for detoxifying xenoestrogens, poor liver function may indicate an inability to process these compounds efficiently.
Glyphosate or Chemical Toxicity Tests
Identifies pesticide and plastic-related chemicals that may contribute to hormone disruption.
If test results show hormonal imbalance, the next step is reducing xenoestrogen exposure and supporting the body’s natural detox pathways.
How to Avoid Xenoestrogens & Detox Naturally
While you can’t completely eliminate xenoestrogens from your environment, you can significantly reduce your exposure with a few practical steps:
1. Switch to Safer Materials
Replace plastic food storage containers and water bottles with glass or stainless steel.
Avoid plastic wraps; use beeswax wraps instead.
2. Choose Clean Personal Care Products
Look for labels like "paraben-free" and "phthalate-free."
Use apps like EWG’s Skin Deep or Think Dirty to evaluate product safety.
3. Opt for Natural Cleaning Products
Use fragrance-free or naturally scented detergents, such as Molly’s Suds or Branch Basics.
Make your own cleaners with simple ingredients like vinegar and baking soda.
4. Avoid Synthetic Fragrances
Choose unscented or naturally scented products for perfumes, candles, and air fresheners.
Look for “phthalate-free” on the label.
5. Eat Organic and Non-GMO Foods
Choose organic produce to avoid pesticides and herbicides.
Prioritize organic or grass-fed meats and dairy products.
6. Filter Your Water
Invest in a water filter to remove contaminants, including hormone-disrupting chemicals.
7. Upgrade Cookware
Replace non-stick cookware with cast iron, stainless steel, or ceramic options.
8. Detox Your Wardrobe
Opt for natural fibers like cotton, wool, or linen over synthetic fabrics.
Tips for Beginners
If this seems overwhelming, start small. Here are some ideas to ease into the process:
Focus on What You Can Control
You can’t avoid every source of xenoestrogens, but reducing exposure where possible is a step in the right direction.Start with One Change at a Time
For example, replace your plastic water bottle first. Once that habit sticks, move on to safer personal care products.DIY When Possible
Make simple swaps like creating your own all-purpose cleaner with equal parts vinegar and water, plus a few drops of essential oil.Look for Affordable Options
Brands like Dr. Bronner’s and Seventh Generation offer clean, budget-friendly alternatives to conventional products.
Support Your Body’s Detox Processes
Even with the best efforts, some exposure to xenoestrogens is inevitable. You can support your body’s natural detoxification with these tips:
Drink Plenty of Water: Staying hydrated helps flush toxins from your system.
Eat Cruciferous Vegetables: Foods like broccoli, kale, and Brussels sprouts support liver detoxification.
Stay Active: Exercise encourages sweating, which helps remove toxins.
Consider Supplements: Compounds like DIM (diindolylmethane) can help metabolize estrogen; consult a healthcare provider first.
Resources for Safer Living
For further guidance and recommendations, check out these trusted resources:
Environmental Working Group (EWG): www.ewg.org
Think Dirty App: A mobile app for evaluating the safety of personal care and household products.
Books:
Estrogeneration by Anthony Jay: Explores the impact of estrogenic chemicals on health.
Encouragement for the Journey
Switching to a low-tox lifestyle doesn’t have to happen overnight. Every small change you make reduces your exposure and contributes to better long-term health. Focus on progress, not perfection. Remember: starting with just one swap—like using a glass water bottle or fragrance-free detergent—is a meaningful step toward a healthier life.
With knowledge and intention, you can take control of your health and protect yourself and your family from harmful xenoestrogens.
Want help actually removing these toxins from your home and daily routine?
My Bye Bye Toxins Guide walks you through identifying and reducing common environmental toxins — including plastics, synthetic fragrances, cleaning products, and everyday exposures that contribute to hormone disruption.